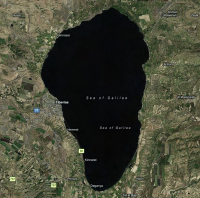
The Sea of Galilee is Israel's largest freshwater lake, approximately 53 kilometers (33 miles) in circumference, about 21 km (13 miles) long, and 13 km (8 miles) wide; it has a total area of 166 km², and a maximum depth of approximately 43 meters. At 209 meters below sea level, it is the lowest freshwater lake on Earth and the second-lowest lake in the world after the Dead Sea, a saltwater lake. It is not a sea by any normal definition; it is called a sea by tradition. The lake is also known on modern maps as Lake Galilee or Lake Tiberias. The name Galilee refers to the region of Galilee in which it is located. In modern Hebrew it is known by its biblical name, Yam Kinneret (ים כנרת), "Sea of Kinnereth" (Numbers 34:11; Joshua 13:27). The name may originate from the Hebrew word kinnor ("harp" or "lyre") - which the lake's shape resembles. It has also been called the Lake of Gennesaret or the Sea of Gennesaret (Greek: Γεννησαρέτ Strong's G1082 - Gennēsaret, of Hebrew origin, cf H3672 כנרות Kinnĕrowth, Chinneroth or Cinneroth or Chinnereth = "harps"). (Luke 5:1) after the name of a small fruitful plain which lies on its western side.
The Kinnĕrowth is fed by underground springs, but its main source is the Jordan River, which flows through it from north to south.
No comments:
Post a Comment